Additional packages
Scripting package
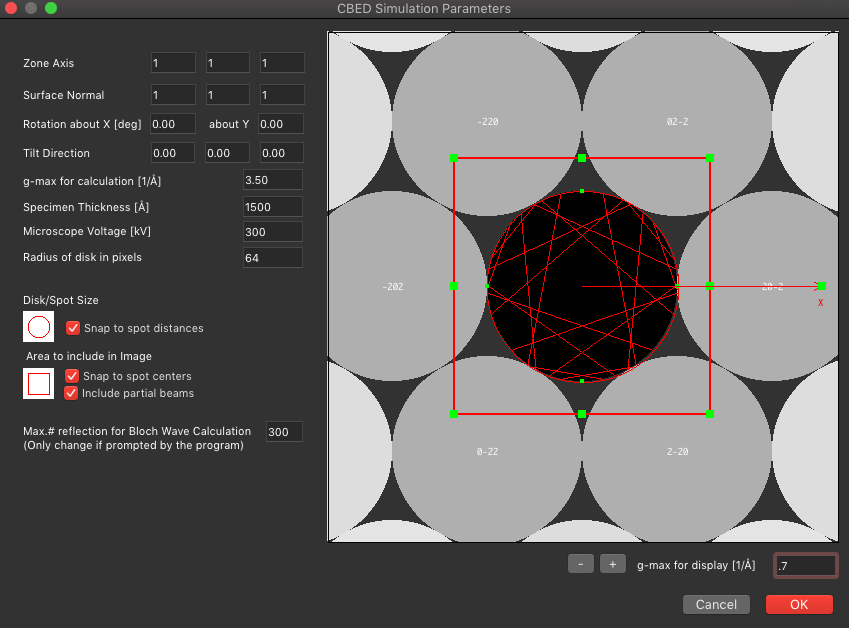
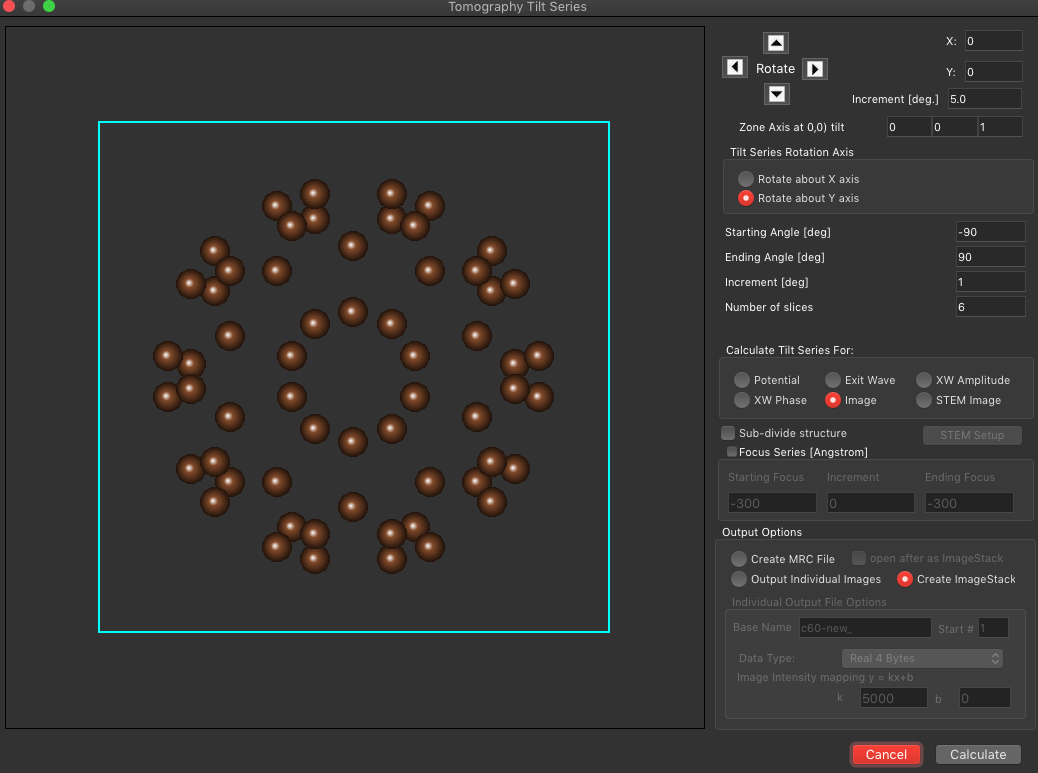
Scripting is a powerful way to extend the functionality of Tempas by controlling the simulation or processing of images in an automated way. One can create completely new algorithms to test out or implement new ideas.
The scripting language for Tempas will be familiar to anyone who has ever created a program in C, C++ or has some experience with the scripting language for Digital Micrograph (copyright Gatan Inc.). In order to facilitate the creation of scripts for someone who has created scripts for Digital Micrograph, the scripting language has built in functions which will allow many DM scripts to be run without any (or few) modifications.
Learn more →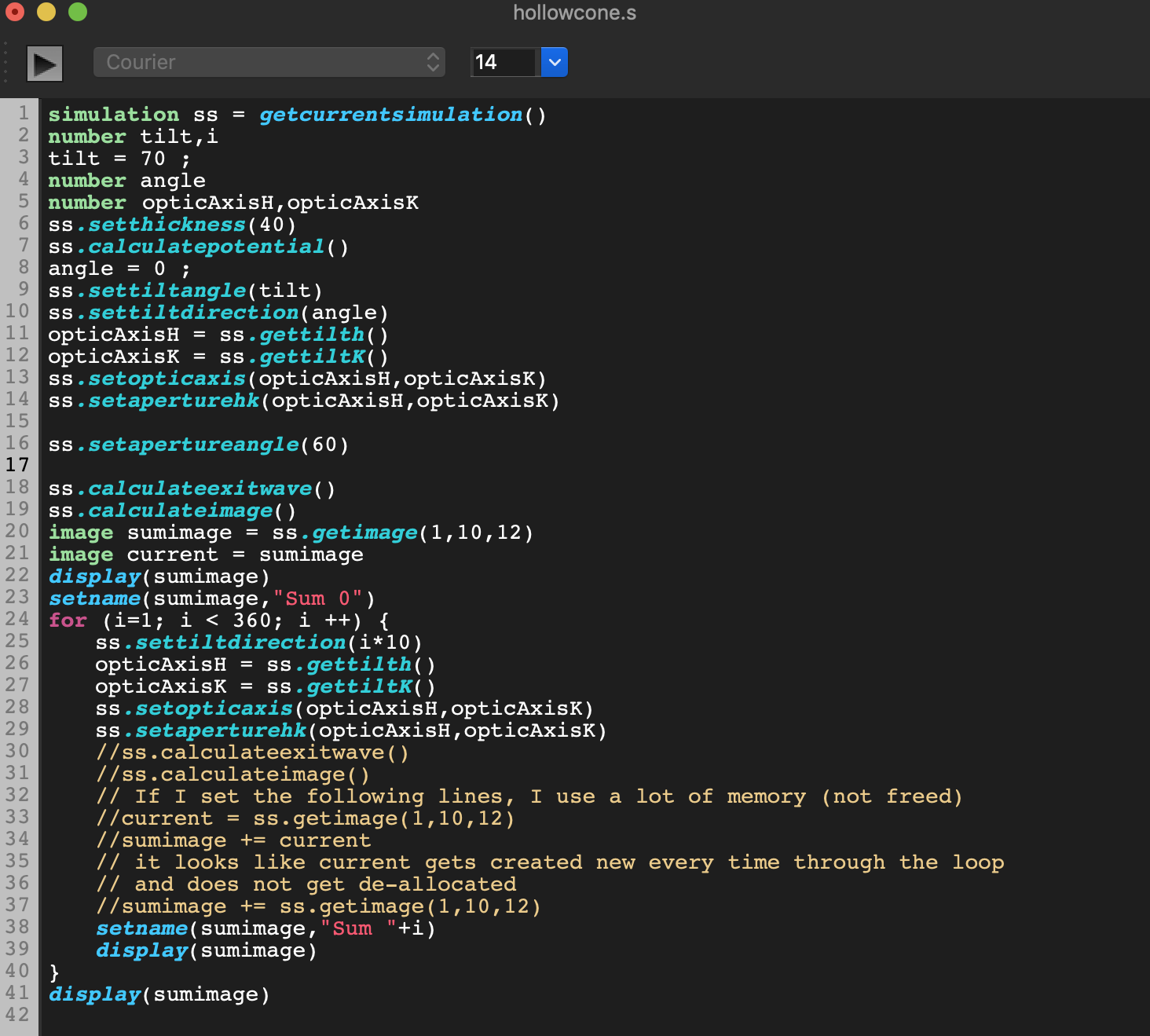
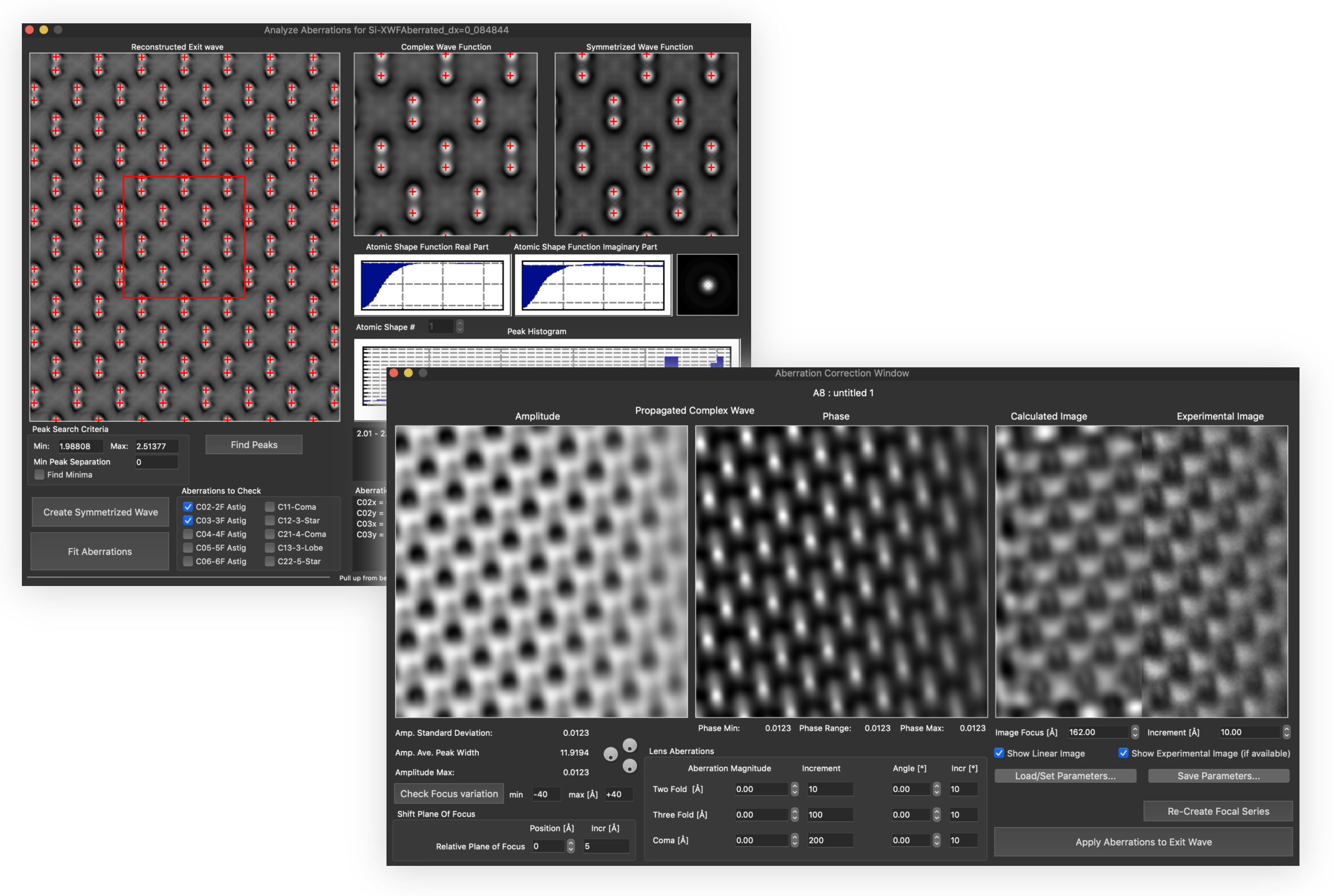
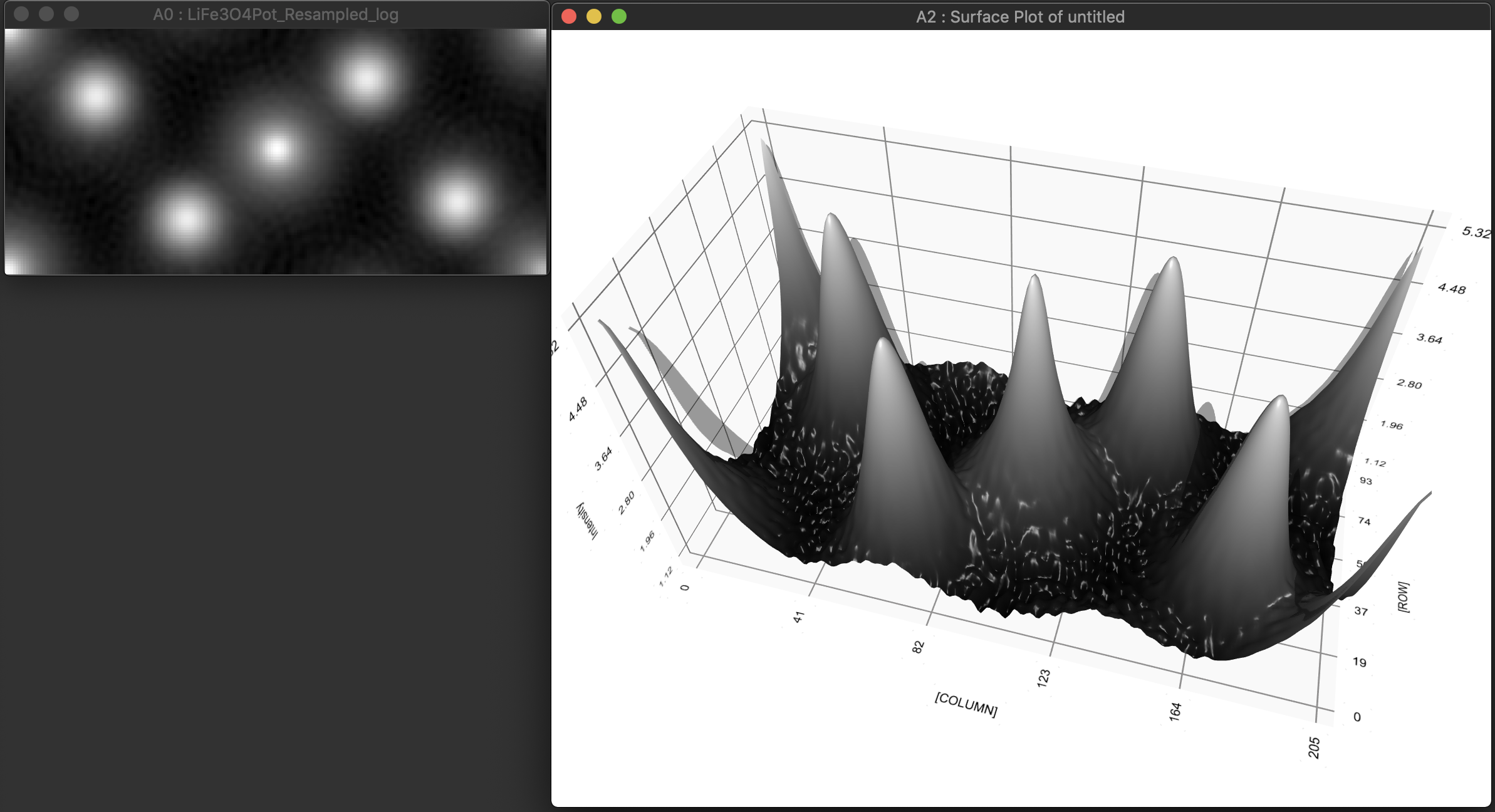
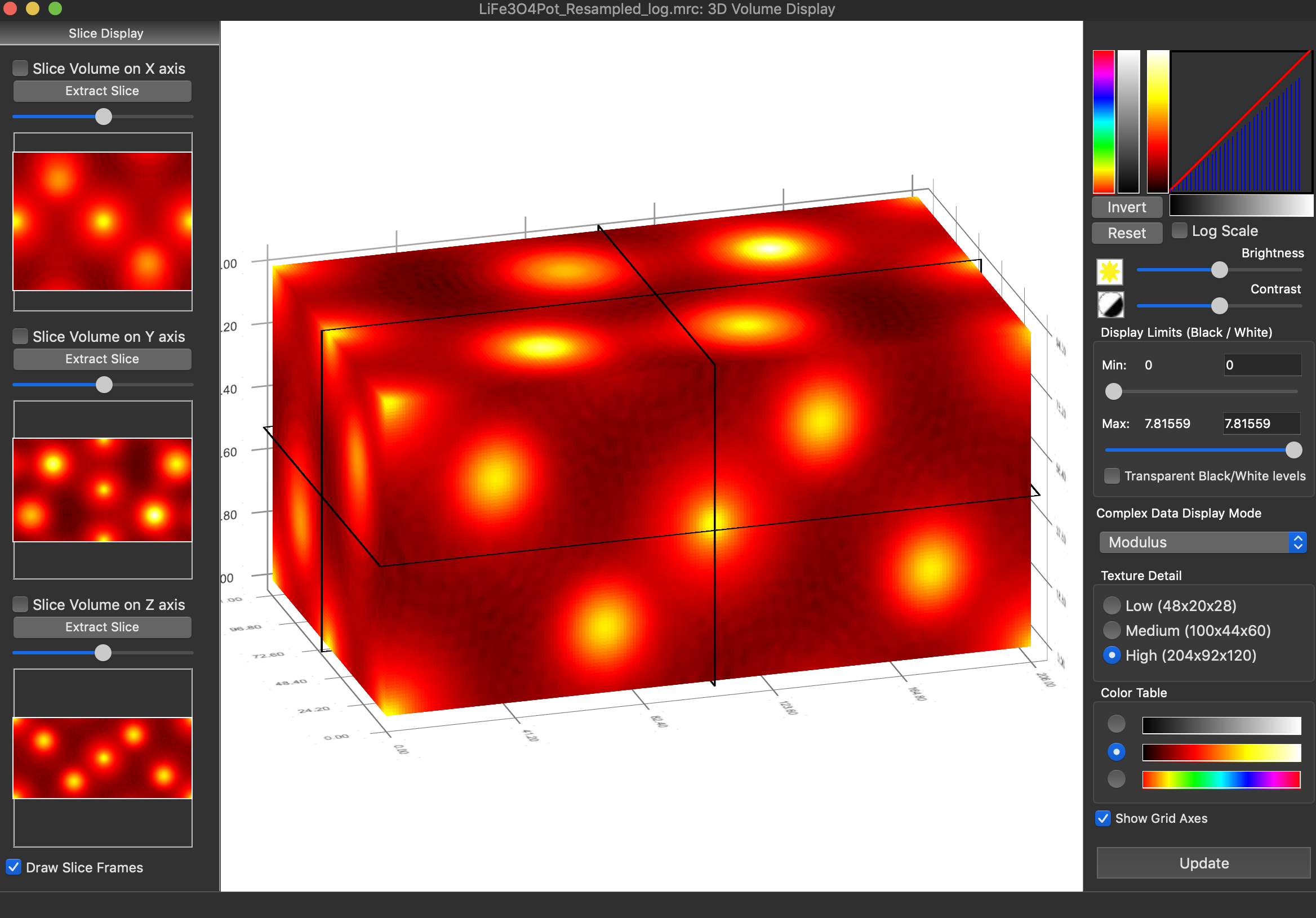
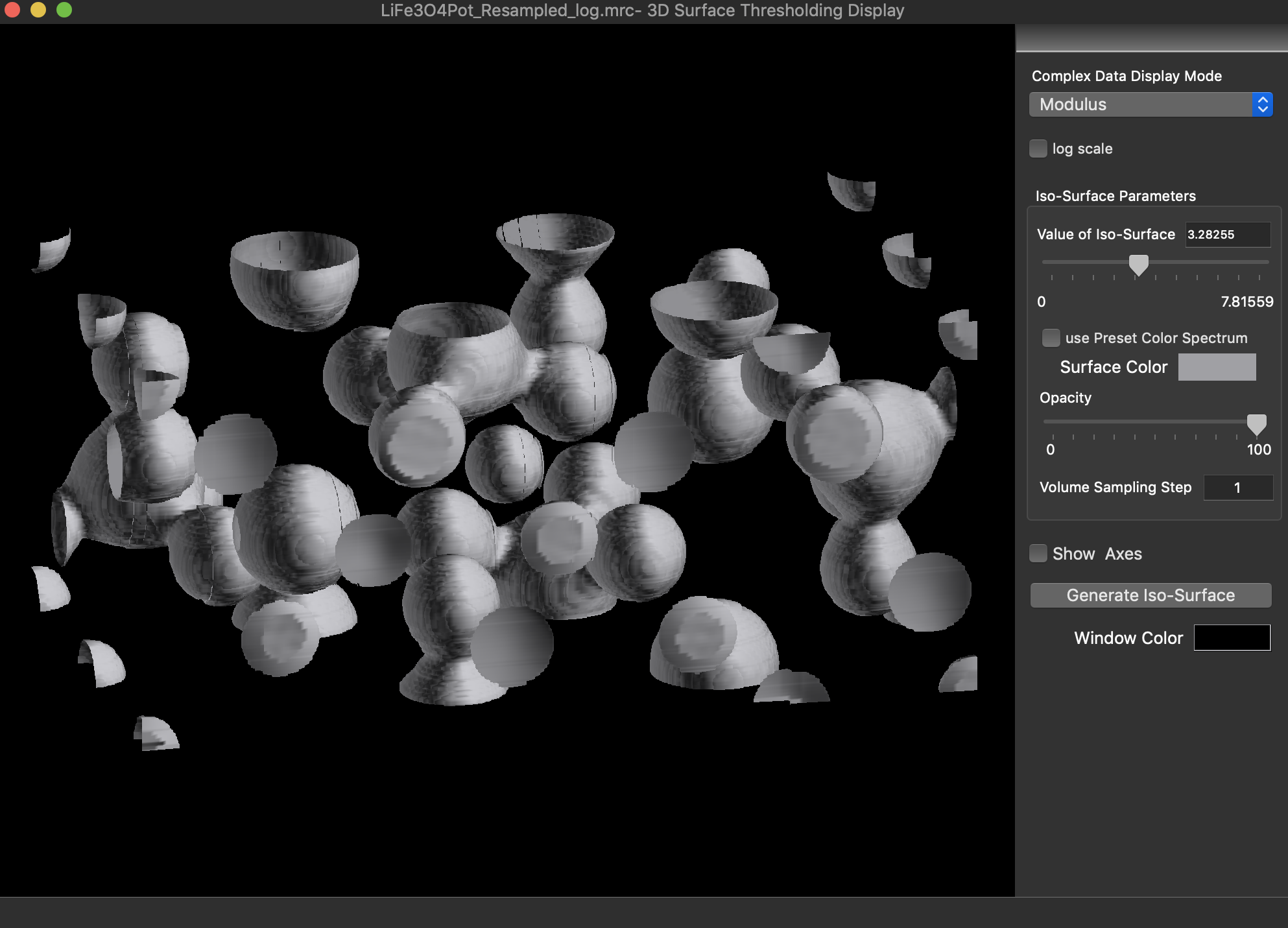
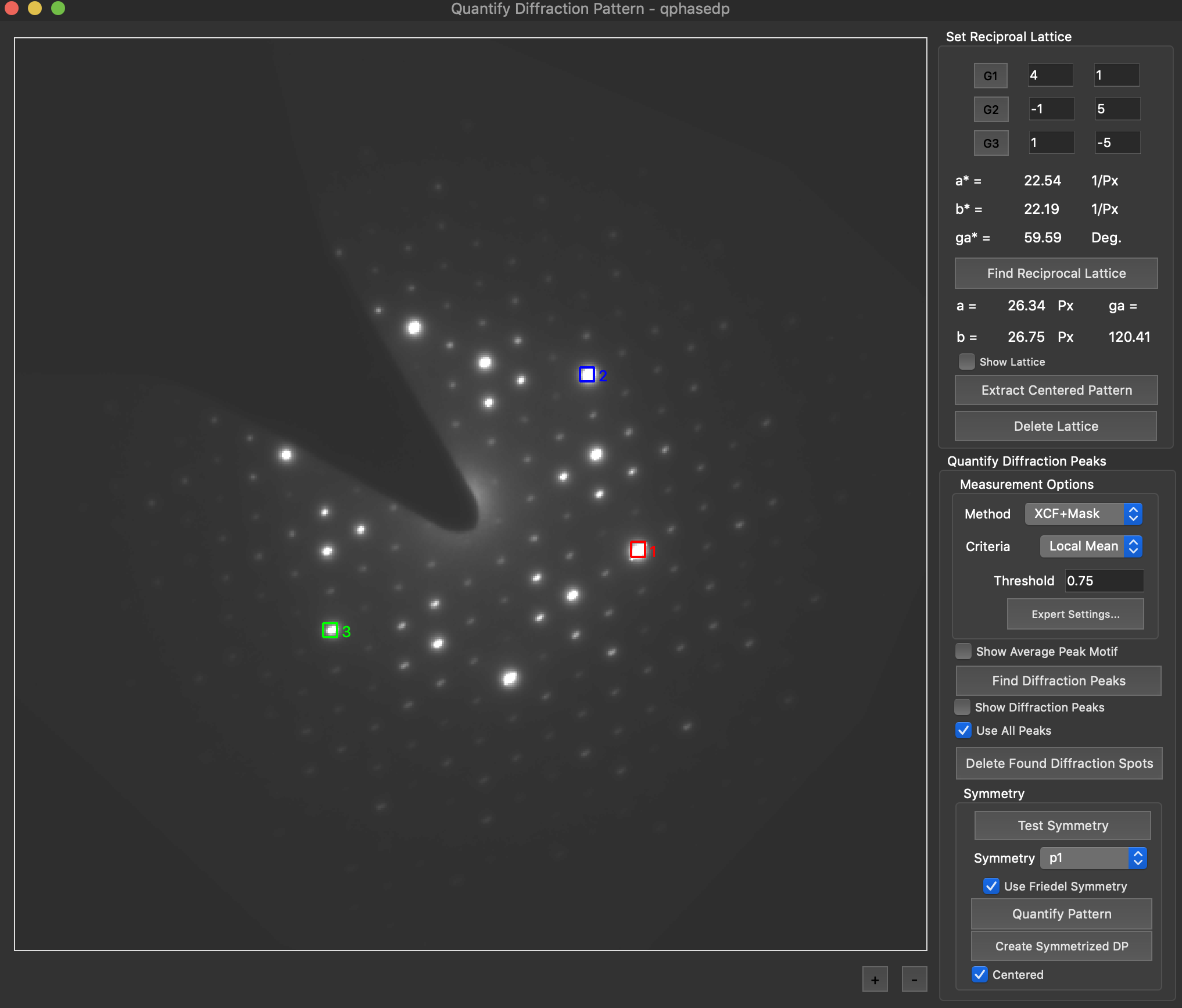
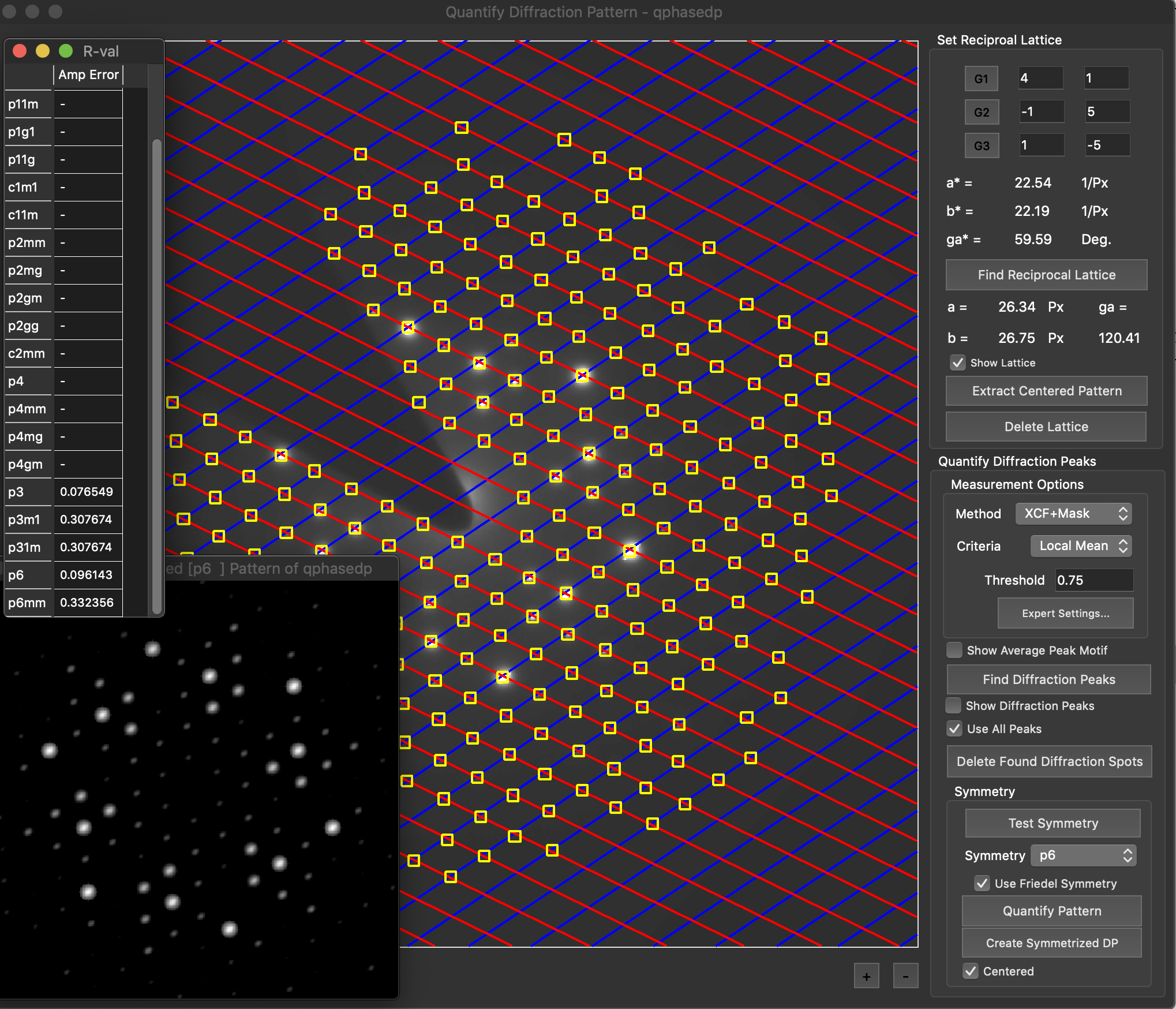
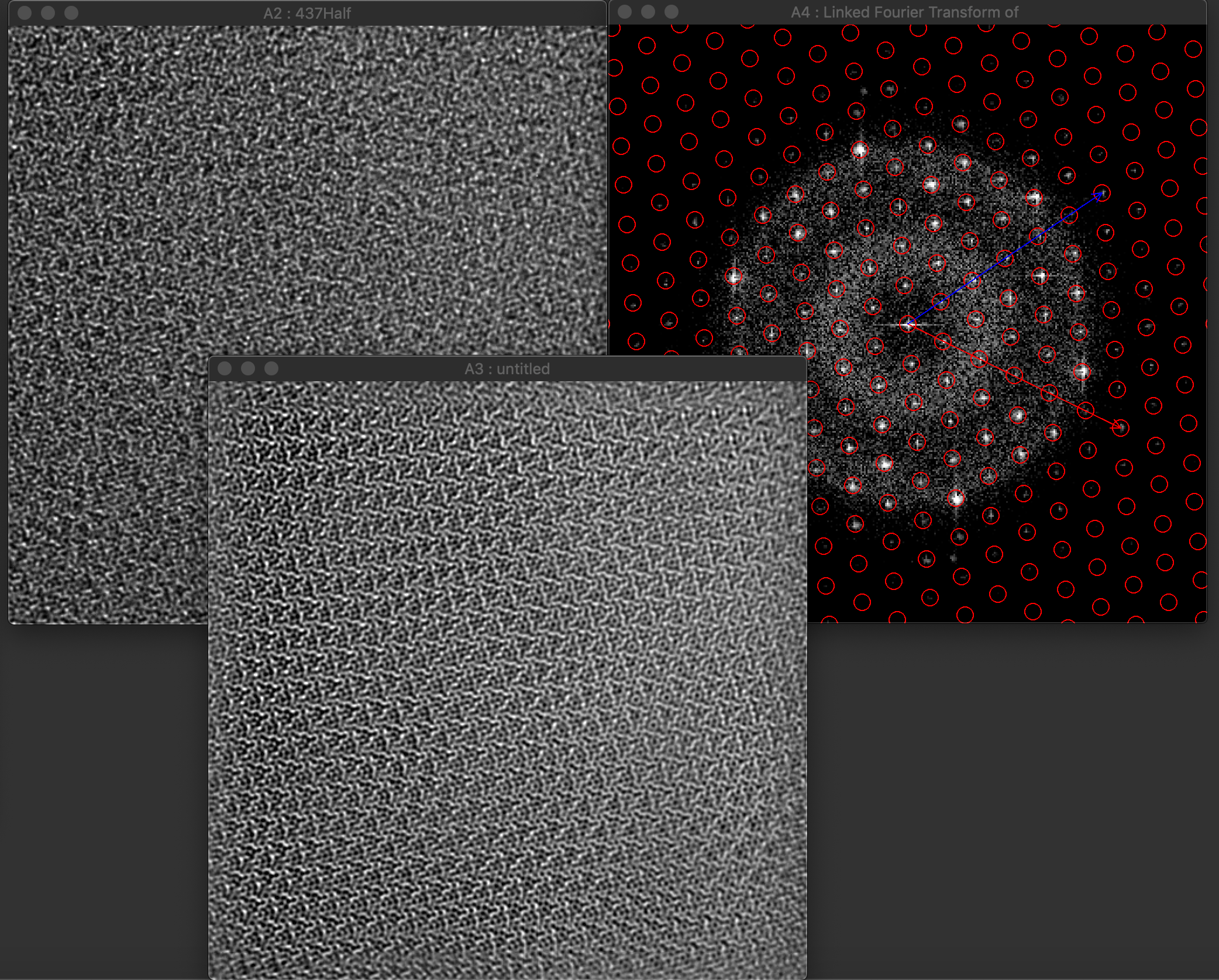
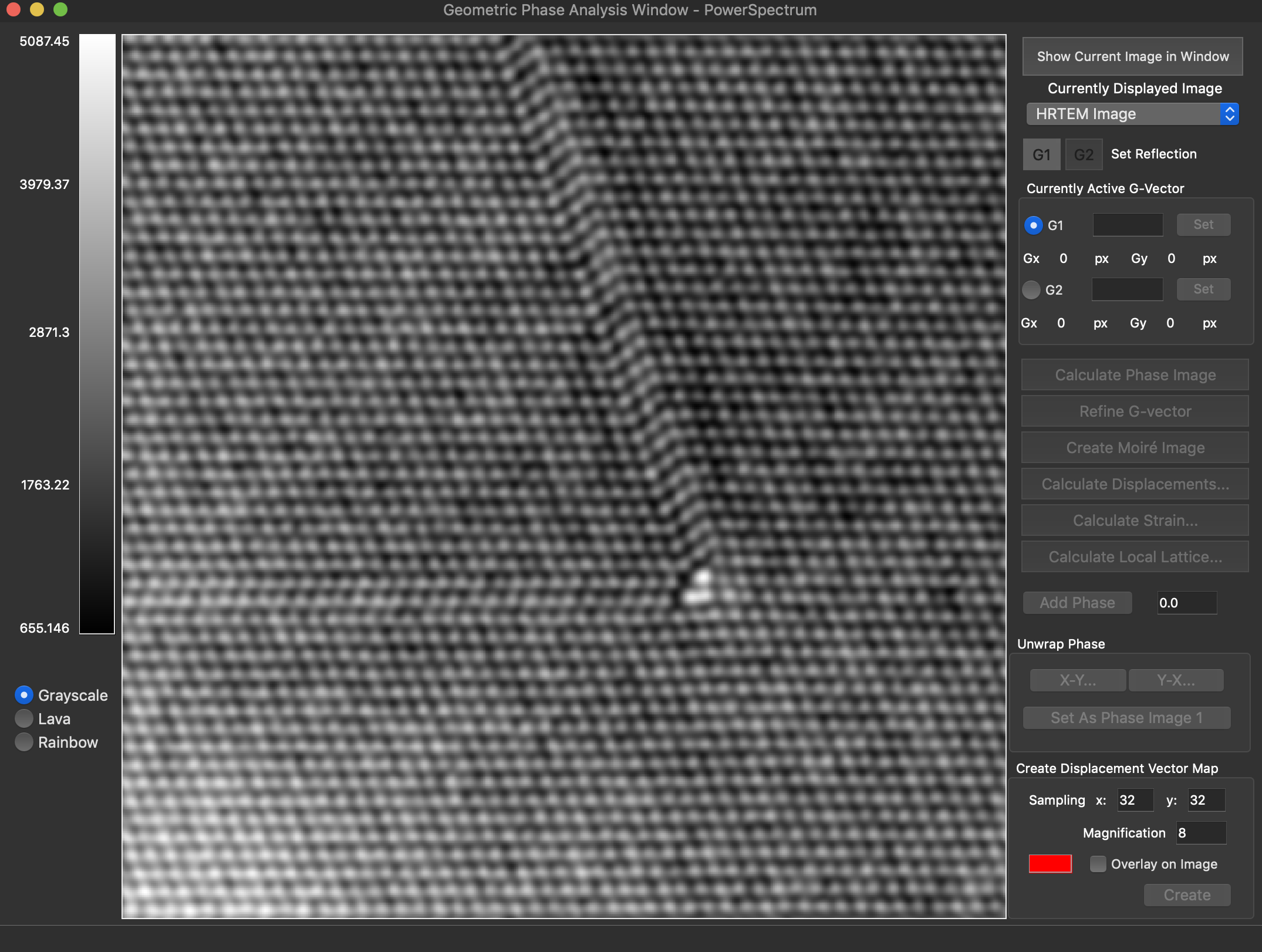
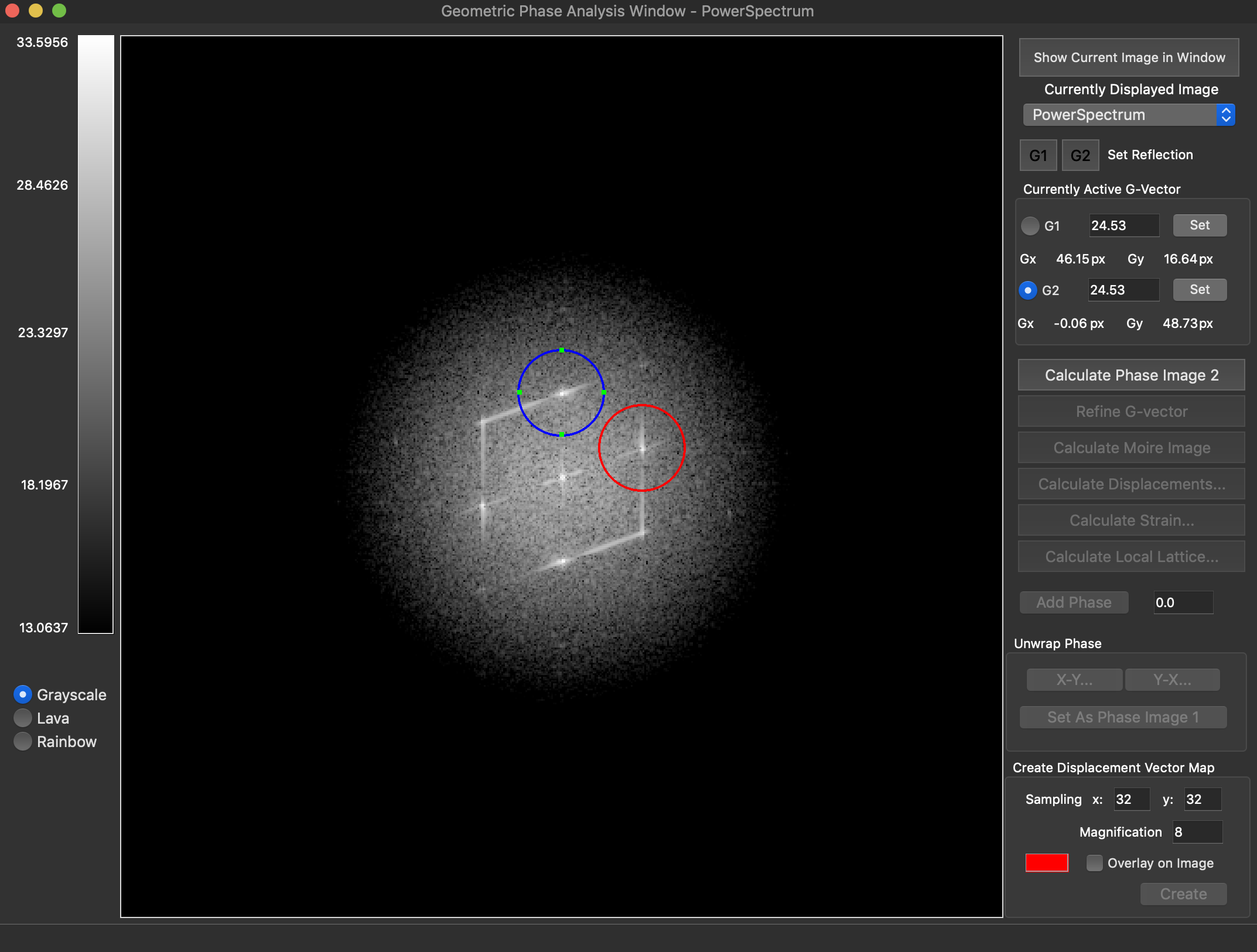
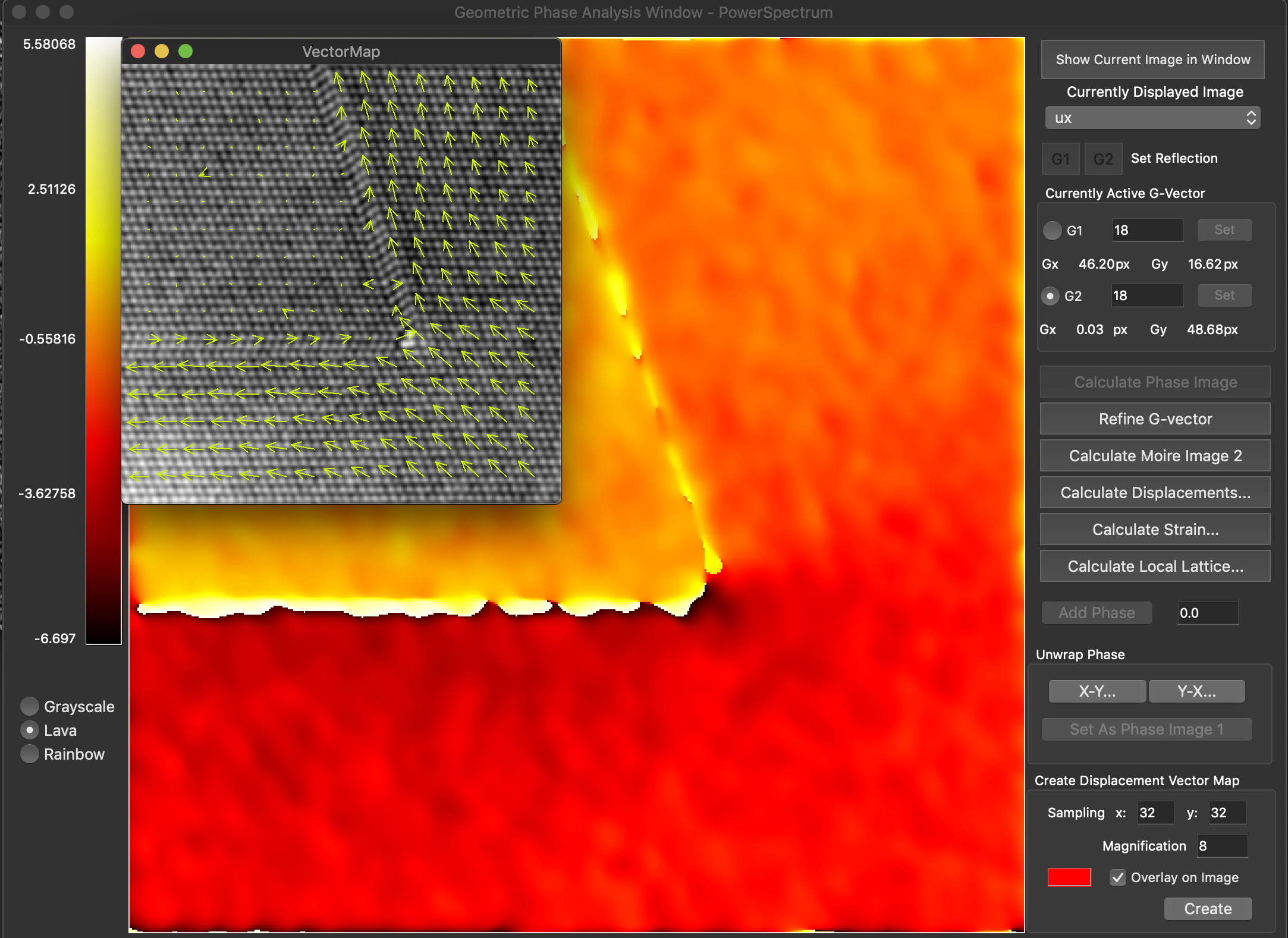
Reconstruction package
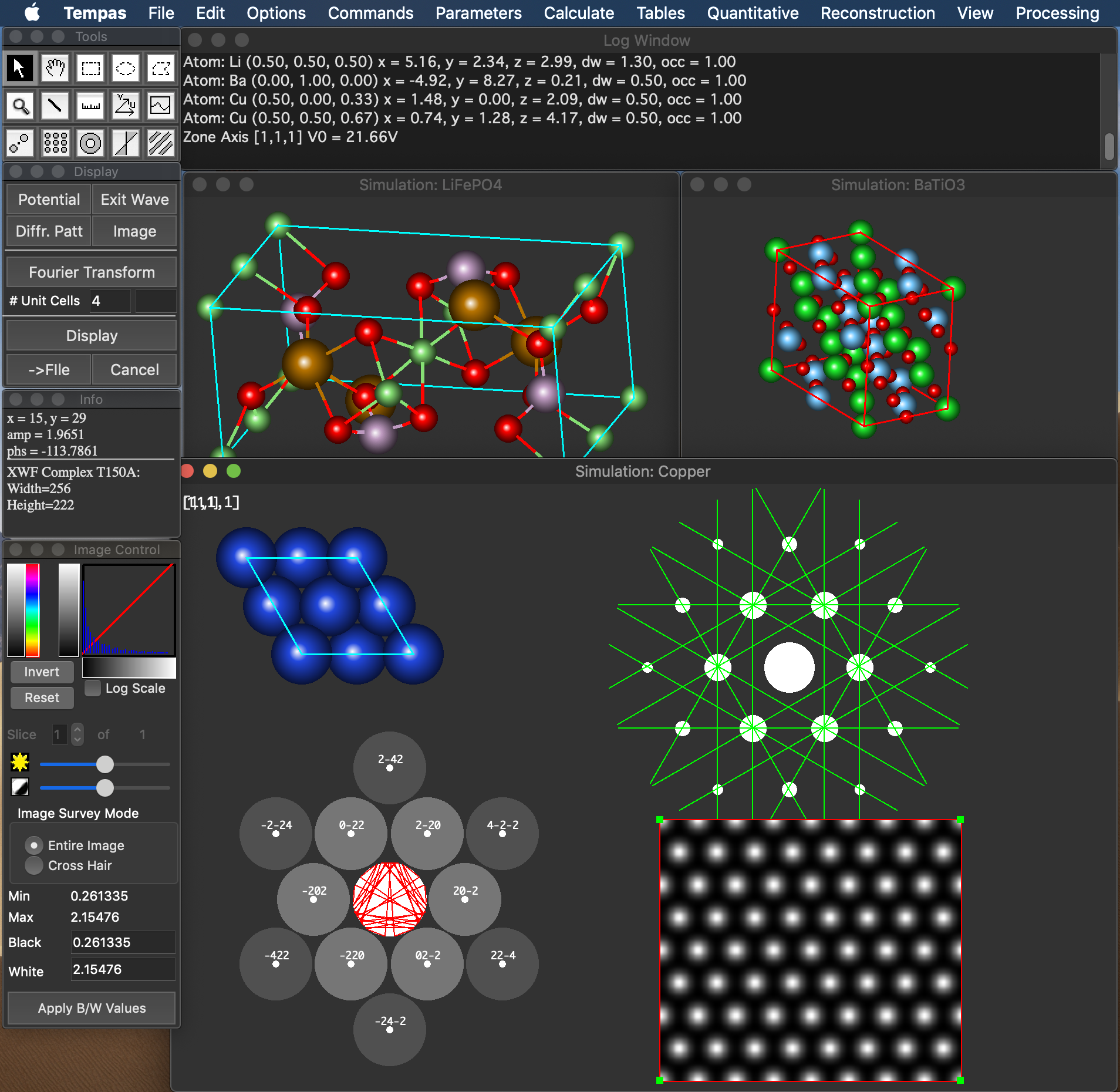
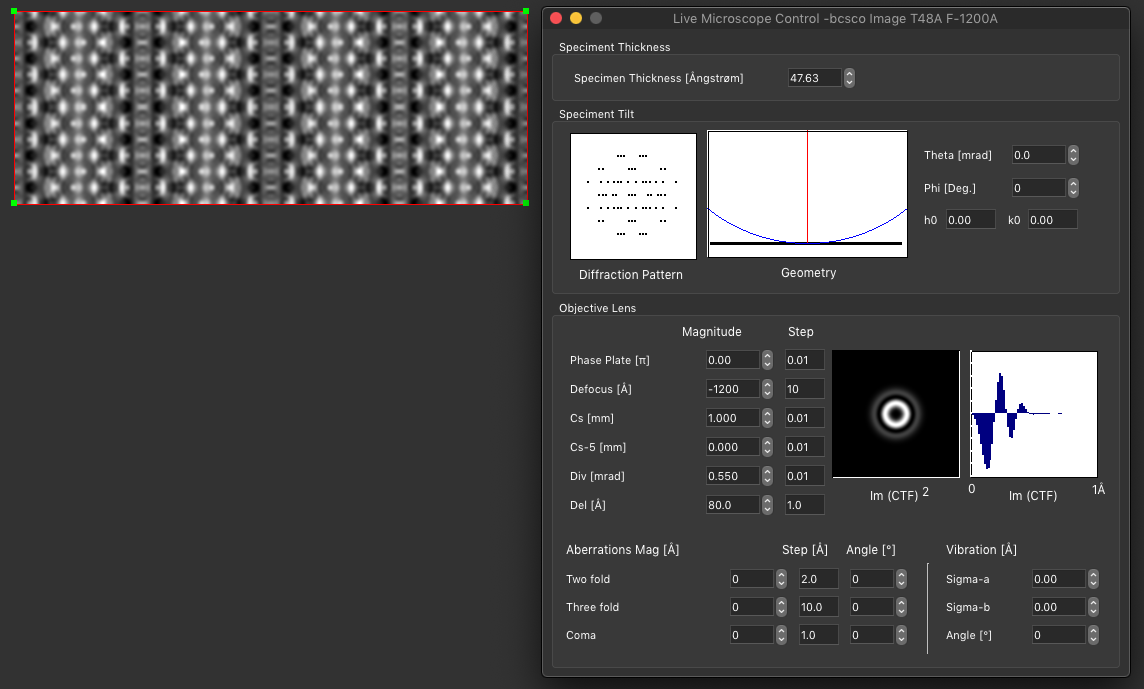
The reconstruction software package consists of algorithms for obtaining exit wave functions and the specimen potential from a thru-focus-series together with aberration correcting phase plates, image alignment, Shiske filter object restoration.
Learn more →